National Income At Current Price (Nominal National Income)/ Nominal GDP
• It refers to the money value of final goods and services produced by nominal residents of a country in a year, measured at current year prices.
• For example measurement of India’s national income of 2019-2020 at the price of 2019-2020.
• Also known as nominal national income.
• It does not depict the true picture of the country’s economic growth as an increase in nominal national income is due to an increase in price level without any change in physical output.
NATIONAL INCOME AT CONSTANT PRICE (Real National Income) / Real GDP
• It refers to the money value of all the final goods and services produced by nominal residents of a country in a year, measured at base year price.
• For example, measurement of India’s national income 2019-2020 at a price of 2012-2013
• It is also known as real income
• It shows the true picture of the economic growth of a country as an increase in real income is due to an increase in physical output not due to a change in the price level.
| NOMINAL GDP | BASIS OF COMPARISON | REAL GDP |
| It is the sum total of economic output produced in a year computed at current market prices. | Meaning | It is the sum total of economic output produced in a year computed at some specific base year. At present, it is 2011-2012. |
| It fluctuates due to changes in general price level change inflow of goods and services | Fluctuations | It fluctuates due to change in output level i.e., the flow of goods and services only general price level remain constant. |
| Nominal GDP does not take inflation into account. | Adjusted for inflation | Real GDP is inflation-adjusted GDP. |
| Calculated by multiplying current year output with current year price. | Calculation | Calculated by multiplying current year output with base year price, i.e., constant price. |
| It is comparatively greater than real GDP as current year prices are taken into effect. | Value of GDP | It is much lower. Since it is calculated at base-year prices. |
| It can be compared with various quarters of the given year. | Utility | It can be compared with two or more fiscal years. |
| Nominal GDP is not the true indicator of economic growth. | Economic growth | Real GDP is known to be the true indicator of economic growth. |
GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT DEFLATOR
This GDP deflator, also known as implicit price deflator, is a measure of inflation. It is the ratio of the value of goods and services an economy produces in a particular year at current prices to that of prices that prevailed during the base year. The GDP deflator exhibits how much a change in GDP relies on changes in the price level.
For example, say India produced $ 2 trillion worth of goods and services in 2017-2018 and $ 2.5 trillion in 2018-2019. On the surface, it seems that the output grew by 25% year on year. However, if we assume prices rose by 10% from year one to year two, the $2.5 trillion figure would be inflated by 10% automatically when compared to year one i.e., 2017-2018. Therefore, ignoring the rate of inflation (increase in prices) the economy only grew by 15% compared to year one to year two.
So in the above-mentioned case, the “Nominal GDP” for the year 2018-2019 would be $ 2.5 trillion while “Real GDP” would be $ 2.3 trillion ($ 2 trillion + 15% after adjustment of inflation i.e. 10% of $ 2 trillion).
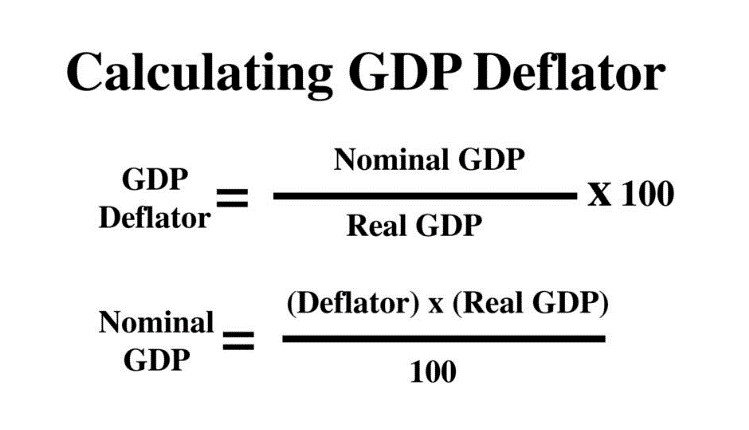
Symbolically,
In above case,
GDP deflator = 2.5 × 100 = 108.69
In this way, the GDP deflator is significant because when GDP for two different years is compared without an inflation adjustment, it can provide deceptive results. In other words, an economy that is experiencing price inflation would appear to be growing in monetary terms. However, that same economy might be exhibiting little to no growth, if prices are kept constant (rate of inflation).
IMPORTANT POINTS ABOUT GDP DEFLATOR
- The GDP deflator is a price index that measures inflation or deflation in an economy by calculating a ratio of nominal GDP to real GDP.
- The GDP deflator is a more comprehensive inflation measure than the consumer price index (CPI) because it is not based on a fixed basket of goods and services.
- GDP deflator is allowed to change from year to year with people’s consumption patterns, investment patterns or the introduction of new goods and services.
- GDP deflator includes only those which have been produced domestically, imported goods are not the part of GDP.
Very informative
Thanks! Glad U Liked It!
Things have been explained in easy language. This is a really helpful content. It covers almost everything about the topic. Nice work!!